How to Identify Fatty Liver Disease’s Early Symptoms
Overview
An outline of fatty liver disease in brief
The significance of early detection
Who is in danger?
Comprehending Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease: what is it?
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) are the two types.
Typical reasons and danger signs
The initial signs of fatty liver disease
1. Inexplicable Weakness and Fatigue
How energy levels are impacted by liver dysfunction
Why early weariness is frequently disregarded
2. Upper Right Abdominal Pain or Discomfort
Where the liver is located and why it hurts
When to need medical help
3. Inexplicable Weight Gain or Loss
How metabolism is disrupted by a fatty liver
Relationship between weight swings and insulin resistance
4. Bloating and Digestive Problems
The impact of the liver on digestion
Symptoms include as bloating, nausea, and appetite loss
5. Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
When liver disease develops from fatty liver
How jaundice is a sign of a major issue
Observable and Physical Indications to Look Out for
6. Pale stools and dark urine
What color shifts signify the health of the liver?
When to act
7. Leg and abdominal swelling (edema and ascites)
Retention of fluids as an indication of liver disease
Why the liver finds it difficult to control fluid levels
8. Skin Alterations: Red palms, rashes, and itching
The liver’s function in cleansing and its impact on the skin
Advanced fatty liver disease symptoms
Medical Evaluation and Diagnostic Testing
Blood testing (ALT, AST, and liver function tests)
Imaging tests (MRI, FibroScan, Ultrasound)
For severe situations, a liver biopsy
How to Avoid and Treat Fatty Liver Disease
Changes in lifestyle and a nutritious diet
The value of consistent exercise
Controlling risk factors such as obesity and diabetes
When to Consult a Physician
Warning indicators that need to be addressed right away
The value of routine examinations
In conclusion
The significance of identifying early indicators
Taking initiative to enhance liver health
FAQs
Is it possible to reverse fatty liver disease?
What is the duration of development for fatty liver disease?
In order to prevent fatty liver disease, which foods should I avoid?
Can fatty liver disease lead to additional health issues?
Do persons who are not obese often get fatty liver disease?

How to Identify Fatty Liver Disease’s Early Symptoms
Overview
Millions of people throughout the world suffer from fatty liver disease, which in its early stages shows no signs. It may result in cirrhosis, severe liver damage, or even liver failure if treatment is not received. Because the liver is essential for digestion, metabolism, and detoxification, its malfunction can have a profound impact on the body.
The good news? If detected early, fatty liver disease is reversible. Serious issues can be avoided by being aware of the early warning signals and altering one’s lifestyle. So, how can you spot fatty liver disease’s early symptoms? Let’s get started.
Comprehending Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease: what is it?
When too much fat accumulates in the liver, it can cause fatty liver disease. There is very little to no fat in a healthy liver, but it becomes an issue when it accounts for more than 5–10% of the liver’s weight.
Fatty liver disease comes in two primary forms:
People who drink little to no alcohol may develop non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is frequently associated with poor diet, diabetes, and obesity.
Excessive alcohol usage causes alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD), which results in scarring and inflammation of the liver.
If left untreated, fatty liver disease of any kind can develop into more serious disorders, including cirrhosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
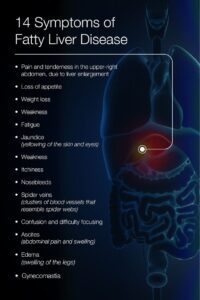 The initial signs of fatty liver disease
The initial signs of fatty liver disease
1. Inexplicable Weakness and Fatigue
Persistent fatigue is one of the initial indicators of fatty liver disease. The body finds it difficult to maintain regular energy levels when the liver is overloaded with fat because it is essential for energy production and metabolism.
Even after getting a full night’s sleep, you could still feel exhausted.
Even simple everyday chores can appear draining.
Brain fog and trouble focusing can be symptoms of chronic weariness.
Fatigue is sometimes disregarded because it is a typical symptom of many illnesses. It’s worthwhile to talk to your doctor about it, though, if it continues along with other symptoms.
2. Upper Right Abdominal Pain or Discomfort
The liver is situated directly behind the rib cage in the upper right section of the abdomen. The liver becomes irritated as fat builds up, which results in discomfort or slight pain there.
Instead of being intense, pain is typically dull and continuous.
After consuming alcohol or fatty foods, it can get worse.
Some report experiencing a sensation of pressure or fullness in their upper abdomen.
Even if sporadic discomfort might not appear concerning, persistent pain needs to be examined by a medical expert.
3. Inexplicable Weight Gain or Loss
Because fatty liver disease alters metabolism, weight fluctuations can be unanticipated:
Unexpected weight loss: Muscle loss and abrupt weight loss are caused by the liver’s inability to digest nutrition.
Unexpected weight gain: Insulin resistance is frequently linked to hepatic fat buildup, which facilitates weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
Weight fluctuations without dietary or activity modifications may indicate liver impairment.
4. Bloating and Digestive Problems Liver dysfunction can cause digestive problems, which might result in:
Gas accumulation and bloating
nausea, particularly after consuming food
Lack of appetite or experiencing fullness too soon
Bile, which is produced by the liver, aids in the digestive system’s breakdown of lipids. Digestion slows down when it is compromised, which is uncomfortable.
5. Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
Even though jaundice indicates advanced liver disease, it can occasionally manifest earlier:
Both the skin and the eye whites become yellow.
The color of urine darkens.
Pale stools and itchy skin might also happen.
When bilirubin, a yellow pigment, accumulates in the blood as a result of liver disease, jaundice results. As soon as you observe these signs, get medical help.
Physical and Observable Symptoms to Look Out for: 6. Pale stools and dark urine
Color changes in the feces and urine are frequently early signs of liver disease. Bilirubin, a chemical that gives bile its color and, in turn, the color of urine and stool, is processed by the liver.
Dark urine: An elevated blood level of bilirubin may be the cause of darker-than-normal urine, such as that of tea or cola.
Pale or clay-colored stools: Soils lose their typical brown hue and might take on a pale, grayish, or clay-like appearance when the liver is unable to produce enough bile.
These alterations could be a symptom of inflammation, bile duct obstructions, or early liver disease. See a doctor right away if you observe consistent changes in the color of your feces or urine.
7. Leg and abdominal swelling (edema and ascites)
Fluid retention brought on by liver illness might result in observable swelling in the lower limbs and belly.
Ascites, or fluid accumulation in the abdomen: Excess fluid can build up in the abdominal cavity as a result of the liver’s inability to control proteins and fluids, giving the appearance of a bloated or enlarged belly.
Edema, or swelling in the legs and feet, is caused by a disruption in fluid balance caused by impaired liver function.
Although they can appear earlier if liver function rapidly deteriorates, these symptoms usually appear in the later stages of fatty liver disease. If you have unexplained bloating or persistent swelling, get medical help.
8. Skin Alterations: Red palms, rashes, and itching
Toxin removal from the blood is a critical function of the liver. Toxins build up in the body when liver function deteriorates, resulting in obvious skin changes:
Pruritus, or persistent itching, is a condition where bile salt buildup in the skin causes constant itching, which is frequently worst at night.
Red palms (palmar erythema): These might be warm or itchy, and they are a common indicator of liver disease.
Spider veins, also known as spider angiomas, are dilated blood vessels that frequently form tiny, web-like clusters on the hands, chest, or face.
Although they are frequently disregarded, skin-related symptoms, especially in those with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), can be an early sign of liver issues.

Medical Evaluation and Diagnostic Testing
To evaluate the health of your liver, your doctor might suggest the following tests if you encounter any of these symptoms:
1. Examinations of the blood
Liver enzymes such as ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase) are measured by liver function tests (LFTs). Increased levels could be a sign of liver injury.
Lipid profile: Evaluates the amount of cholesterol, which might lead to fatty liver disease.
Blood sugar tests: NAFLD is frequently associated with insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
2. Imaging Examinations
The most popular non-invasive method for identifying liver fat accumulation is ultrasound.
FibroScan (elastography): Assesses liver stiffness to identify scarring or fibrosis.
MRI or CT scans: Offer comprehensive imaging to evaluate the size, fat content, and any damage of the liver.
3. Liver Biopsy (In Cases That Are Severe)
To determine the extent of fatty liver disease and identify fibrosis or inflammation, a liver biopsy may occasionally be required. This entails removing a tiny sample of liver tissue for microscopic analysis.
How to Avoid and Treat Fatty Liver Disease
Even while fatty liver disease can be dangerous, its advancement can be stopped with early identification and lifestyle modifications. Here’s how:
 1. Maintain a Healthful Diet
1. Maintain a Healthful Diet
Consume more fiber: Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains enhance liver function and digestion.
Cut back on processed foods: Steer clear of trans fats, processed carbohydrates, and sugary drinks.
Eat foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as nuts, seeds, and fish, to help your body absorb healthy fats.
Limit your alcohol intake: Drinking alcohol, even in moderation, can harm the liver.
2. Engage in Regular Exercise
Five times a week, try to get in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as swimming, cycling, or walking.
Strength exercise can lower liver fat buildup and increase metabolism.

3. Control the Underlying Factors
Control blood sugar levels: Blood sugar control is essential if you have diabetes or insulin resistance.
Keep your weight in check: Liver fat can be considerably decreased with even a 5–10% weight loss.
Monitor your cholesterol levels: Elevated triglycerides and cholesterol lead to the accumulation of liver fat.
When to Consult a Physician
You ought to see a physician if you encounter:
Chronic exhaustion or inexplicable weakness
Unaccounted-for weight fluctuations (gain or decreases)
Discomfort or edema in the abdomen
Jaundice (eye and skin yellowing)
Color changes in the feces or urine
Extreme skin changes or itching
Blood testing and routine examinations can help identify liver problems before they worsen. With the right diet, exercise, and medical care, fatty liver disease can be reversed if detected early.
In conclusion
The reason fatty liver disease is frequently referred to as a “silent disease” is that it may manifest itself without obvious symptoms. However, you can take action before the situation develops by being aware of early warning symptoms, such as edema, changes in your skin, exhaustion, and digestive problems.
You can prevent and reverse fatty liver disease by leading a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly. Don’t hesitate to get medical help and take preventative measures if you have any symptoms.
1. Is it possible to reverse fatty liver disease?
Indeed! Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy food, and weight loss help reverse fatty liver disease. The key to avoiding complications is early action.
2. How long does it take for the development of fatty liver disease?
Depending on dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical disorders such as diabetes or obesity, fatty liver disease can develop gradually over months or years.
3. In order to prevent fatty liver disease, which foods should I stay away from?
Steer clear of alcohol, processed foods, sugar-filled beverages, trans fats, and high-carbohydrate items like pastries and white bread. Rather, prioritize lean proteins, healthy fats, and entire meals.
4. Can other health issues be brought on by fatty liver disease?
Indeed, fatty liver disease can cause cirrhosis, fibrosis, inflammation (NASH), liver failure, and even liver cancer if treatment is not received. Additionally, it raises the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
5. Do persons who are not obese often have fatty liver disease?
Indeed, fatty liver disease can occur in non-obese people as a result of poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, insulin resistance, or genetic susceptibility, even if obesity is a major risk factor.
 https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/#/analysis/p405220706
Skip to content
https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/#/analysis/p405220706
Skip to content 
2 thoughts on “How to Identify Fatty Liver Disease’s Early Symptoms”