Improved Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment with New European Guidelines
Synopsis
Greetings
An overview of HCC, or hepatocellular carcinoma
The significance of revised European regulations
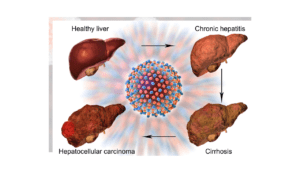
A Comprehensive Overview of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
What is HCC?
Reasons and danger signs
Signs and diagnosis
The Need for Revised Policies
HCC incidence is on the rise in Europe.
Limitations of earlier therapeutic modalities
The part that technology and research play
Important Aspects of the New European Guidelines
The importance of early screening and detection
Better criteria for diagnosis
Tailored treatment regimens
Strategies for Early Detection and Surveillance
High-risk populations for HCC
Tests for screening that are advised
The advantages of early detection
Improvements in Diagnostic Methods
The function of imaging technologies (CT, ultrasonography, MRI)
HCC biomarkers in the early stages
The value of a liver biopsy
HCC Staging System Update
The Liver Cancer Clinic Barcelona (BCLC) system
Updates to improve the distribution of treatments
Techniques for Surgical Treatment
Who can have surgery?
Advantages and disadvantages of resection
Instructions for liver transplantation
Treatments at the Locoregion
Chemoembolization inside the bloodstream (TACE)
Radiation therapy in the airways (TARE)
RFA, or radiofrequency ablation
Comprehensive Treatments for Advanced HCC
Specific treatment (Sorafenib, Lenvatinib)
Possible immunotherapy treatments (Bevacizumab, Atezolizumab)
Combination treatments to improve results
The Function of Personalized Medicine in the Management of HCC
The impact of genetic profiling on treatment decisions
Customizing treatments according to tumor properties
Control of Side Effects of Treatment
Typical side effects of therapy for HCC
Methods for handling complications
Using a Multidisciplinary Approach to Treat HCC
The value of taking a team-based approach
Hepatologists’, oncologists’, and surgeons’ roles
Future Paths in the Treatment of HCC
New treatments and clinical studies
Possible application of artificial intelligence (AI) to the management of HCC
Conclusion and Frequently Asked Questions
A synopsis of the main conclusions
Five frequently posed questions
Improved Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment with New European Guidelines
Greetings
Globally, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant health concern and the most prevalent form of primary liver cancer. To improve diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes, the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) and other medical organizations have revised their guidelines in response to the increasing prevalence of HCC in Europe. These updated recommendations guarantee improved patient survival rates and quality of life by taking into account developments in medical research and technology.
A Comprehensive Overview of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
People who have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), cirrhosis, or hepatitis B and C infections are at risk of developing HCC. Since the illness advances in silence, early detection is essential to successful treatment. Jaundice, stomach pain, inexplicable weight loss, and exhaustion are common symptoms.
The Need for Revised Policies
Due to delayed diagnoses and inadequate treatments, there were previously few therapeutic choices for HCC, and survival rates remained low. These issues are intended to be addressed by the new European standards, which emphasize enhanced staging systems, individualized treatment plans, and early detection.
Important Aspects of the New European Guidelines
Enhanced attention on early detection and surveillance
Diagnostic standards were updated to increase precision.
Multidisciplinary care is emphasized for improved therapeutic results.
Addition of more recent immunotherapies and systemic treatments
 Strategies for Early Detection and Surveillance
Strategies for Early Detection and Surveillance
For high-risk individuals, such as those with cirrhosis and ongoing hepatitis B or C infections, the new guidelines advise routine screening. When paired with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood tests, routine ultrasounds can aid in the early detection of HCC, when curative treatments are most successful.
Improvements in Diagnostic Methods
More accurate tumor detection is now possible because of advancements in imaging methods, including contrast-enhanced CT scans and MRI. To confirm the diagnosis, a liver biopsy could be necessary in certain situations. Additionally, the introduction of biomarkers such as des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP), glypican-3, and AFP has improved early diagnosis.
HCC Staging System Update
The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system is still the recommended paradigm for choosing a course of treatment. In order to maximize patient selection for various therapies, the new guidelines offer adjustments.
Techniques for Surgical Treatment
Liver transplantation or surgical excision continues to be the most curative option for patients with early-stage HCC and healthy livers. The revised rules optimize survival advantages by fine-tuning selection criteria.
Treatments at the Locoregion
TACE, TARE, and RFA are examples of locoregional therapy that are essential for intermediate-stage HCC. These therapies aid in tumor shrinkage, allowing patients to receive systemic therapy or surgery.
Comprehensive Treatments for Advanced HCC
In advanced HCC, the revised guidelines stress the value of immunotherapy and targeted medicines. Patient survival rates have increased when atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1) and bevacizumab (anti-VEGF) are used together.
The Function of Personalized Medicine in the Management of HCC
Customized therapy regimens based on tumor-specific features are now possible thanks to developments in genomic profiling. This method reduces adverse effects while increasing treatment efficacy.
Control of Side Effects of Treatment
Fatigue, nausea, and liver damage are just a few of the side effects that might result from HCC therapies. To improve the quality of life for patients, the new guidelines offer suggestions for handling these issues.
Using a Multidisciplinary Approach to Treat HCC
Hepatologists, oncologists, radiologists, and surgeons must work together as a team to provide the best possible care for patients. The guidelines stress the value of interdisciplinary tumor boards in the decision-making process for therapy.
Future Paths in the Treatment of HCC
New therapy alternatives, including gene treatments, innovative immunotherapies, and AI-driven diagnostic tools, are still being investigated in ongoing research and clinical studies.
In conclusion,
The therapy of liver cancer has advanced significantly with the release of the revised European guidelines for the treatment of HCC. Through the integration of sophisticated medicines, early detection measures, and a tailored strategy, these guidelines seek to improve patient outcomes and increase survival rates.
FAQs
What are HCC’s primary risk factors?
Alcohol misuse, NAFLD, hepatitis B and C infections, and chronic liver illnesses all raise the risk of HCC.
What is the diagnosis process for HCC?
Blood testing (AFP), imaging tests (MRI, CT scans), and occasionally liver biopsies are used in the diagnosis process.
Which course of action is best for treating HCC in its early stages?
Cure options include liver transplantation or surgical resection.
Are there any novel approaches to treating advanced HCC?
It is currently advised to use immunotherapies and targeted treatments such as bevacizumab and atezolizumab.
In what ways might HCC be avoided?
Hepatitis vaccine, alcohol abstinence, and liver health maintenance are preventive methods.
 https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/#/analysis/p405220706
Skip to content
https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/#/analysis/p405220706
Skip to content