fatty liver disease types and Related details of fatty liver disease
Fatty Liver Disease in NAFLD
What is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
NAFLD is a type of fatty liver disease that is not related to heavy alcohol use. There are two kinds:
- Simple fatty liver, in which you have fat in your liver but little or no inflammation or liver cell damage. Simple liver fatty acid typically does not get bad enough to cause liver damage or complications.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), in which you have inflammation and liver cell damage, as well as fat in your liver,. Inflammation and liver cell damage can cause fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver. NASH may lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
What is alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is due to heavy alcohol use. Your liver breaks down most of the alcohol you drink, so it can be removed from your body. But the process of breaking it down can generate harmful substances. These substances can damage liver cells, promote inflammation, and weaken your body’s natural defenses. The more alcohol you drink, the more you damage your liver. Alcoholic fatty liver disease is the earliest stage of alcohol-related liver disease. The next stages are alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Symptoms and Causes of fatty liver disease

Who gets fatty liver disease?
You have a greater chance of developing fatty liver disease if you:
- Are of Hispanic or Asian descent.
- You have completed menopause (your periods have stopped).
- Have obesity with a high level of belly fat.
- Have high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
- Have obstructive sleep apnea (a blocked airway that causes breathing to stop and start during sleep).
What causes fatty liver disease?
Some people get fatty liver disease without having any pre-existing conditions. But these risk factors make you more likely to develop it:
- Having overweight/obesity.
- Having type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Having metabolic syndrome (insulin resistance, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and high triglyceride levels).
- Taking certain prescription medications, such as amiodarone (Cordarone®), diltiazem (Cardizem®), tamoxifen (Nolvadex®), or steroids.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease?
People with fatty liver disease often have no symptoms until the disease progresses to cirrhosis of the liver. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Abdominal pain or a feeling of fullness in the upper right side of the abdomen (belly).
- Nausea, loss of appetite, or weight loss.
- Yellowish skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
- Swollen abdomen and legs (edema).
- Extreme tiredness or mental confusion.
- Weakness.
Diagnosis and Tests
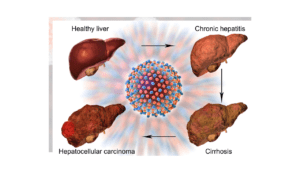
How is fatty liver disease diagnosed?
Because fatty liver disease often has no symptoms, your doctor may be the first to spot it. Higher levels of liver enzymes (elevated liver enzymes) that turn up on a blood test for other conditions may raise a red flag. Elevated liver enzymes are a sign that your liver is injured. To make a diagnosis, your doctor may order:
- Ultrasound or computed tomography (CT scan) to get a picture of the liver.
- Liver biopsy (tissue sample) to determine how far advanced liver disease has progressed.
- FibroScan® is a specialized ultrasound sometimes used instead of a liver biopsy to find out the amount of fat and scar tissue in the liver.
Management and Treatment
How is fatty liver disease treated?
There’s no medication specifically for fatty liver disease. Instead, doctors focus on helping you manage factors that contribute to the condition. They also recommend making lifestyle changes that can significantly improve your health. Treatment includes:
- Avoiding alcohol.
- Losing weight.
- Taking medications to manage diabetes, cholesterol, and triglycerides (fat in the blood).
- Taking vitamin E and thiazolidinediones (drugs used to treat diabetes, such as Actos® and Avandia®) in specific instances.
Prevention
How can fatty liver disease be prevented?
The best way to avoid fatty liver disease is to do the things that maintain overall health:
- Stay at a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, lose weight gradually.
- Exercise regularly.
- Limit your alcohol consumption.
- Take medications as prescribed.
 https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/#/analysis/p405220706
Skip to content
https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/#/analysis/p405220706
Skip to content 
2 thoughts on “Fatty Liver Disease -9 Positive Strategies for fatty liver well being”